Moss Scape
Organizer : Seoul City, Seoul National University
Moss Scape Data Visualization and Installation
SpaceOne Gallery, Seoul, 2018
Moss Scape
Shim + Choi
2018
Shim + Choi
2018
Modern cities face various environmental problems that
threaten human survival. In Korea, countermeasures in
various fields are being discussed due to the seriousness of
fine dust, and it is necessary to discuss and experiment more
fundamentally in order to cope with environmental issues
along with the development of advanced ICT technology. This
paper will closely examine the process of designing and
installing a nature-based media space using environmental
data through the‘Moss-scape’which was exhibited as part
of the ICT Convergence Program organized by Seoul Big
Data Institute. Based on this, this paper examines the
ecological possibility of media to cope with environmental
issue. In order to examine the possibility of media to cope
with urban environmental problems through the utilization of
natural materials, theoretical review of the definition and
scope of media newly presented in the field of media studies
was made. Finally, this paper examines the ecological
possibilities of the media in order to elucidate issues by
analyzing the aesthetic, technological, and social aspects of
the creation and installation process of the moss.
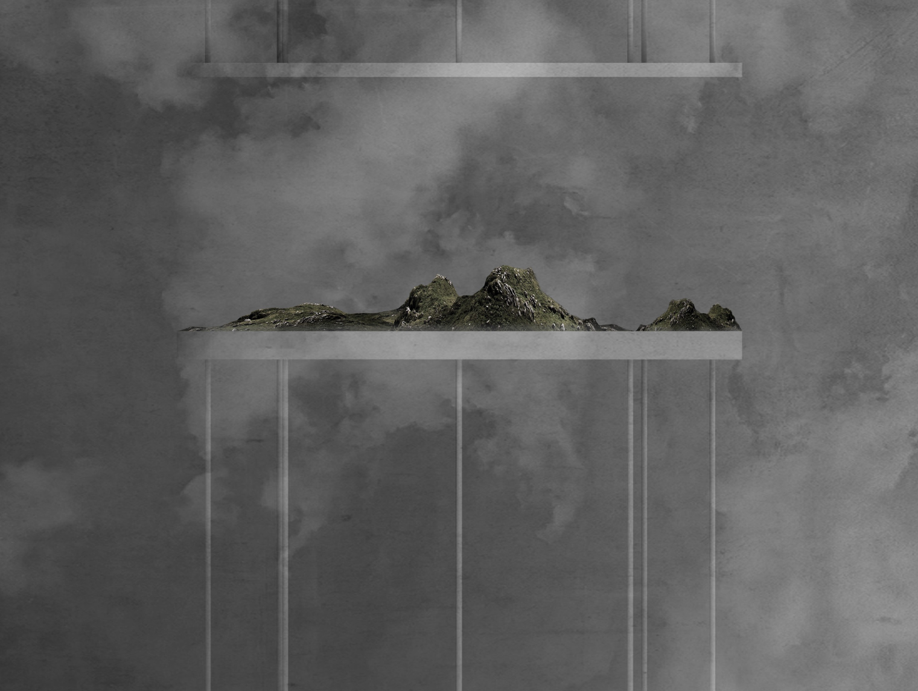

Fine Dust Topographic Map

Process : form Dust-Scape to Moss-Scape
Fine dust data interlocking misting system
The city's 25 districts will be divided into five areas (SE, SW, NE, NW, CTR) and water will be sprayed in proportion to the average PM10 levels of fine dust and real-time PM10 values of fine dust sensor platforms installed in SpaceOne. It was developed using Python language in Raspberry Pi environment. When visitors enter the exhibition hall, a person-sensitive sensormade from 3D printer connected to Raspberry Pi recognizespeople and uses OpenAPI, which is fine dust provided by Air Korea, to obtain PM10 levels of fine dust in real time.
![]()
The city's 25 districts will be divided into five areas (SE, SW, NE, NW, CTR) and water will be sprayed in proportion to the average PM10 levels of fine dust and real-time PM10 values of fine dust sensor platforms installed in SpaceOne. It was developed using Python language in Raspberry Pi environment. When visitors enter the exhibition hall, a person-sensitive sensormade from 3D printer connected to Raspberry Pi recognizespeople and uses OpenAPI, which is fine dust provided by Air Korea, to obtain PM10 levels of fine dust in real time.
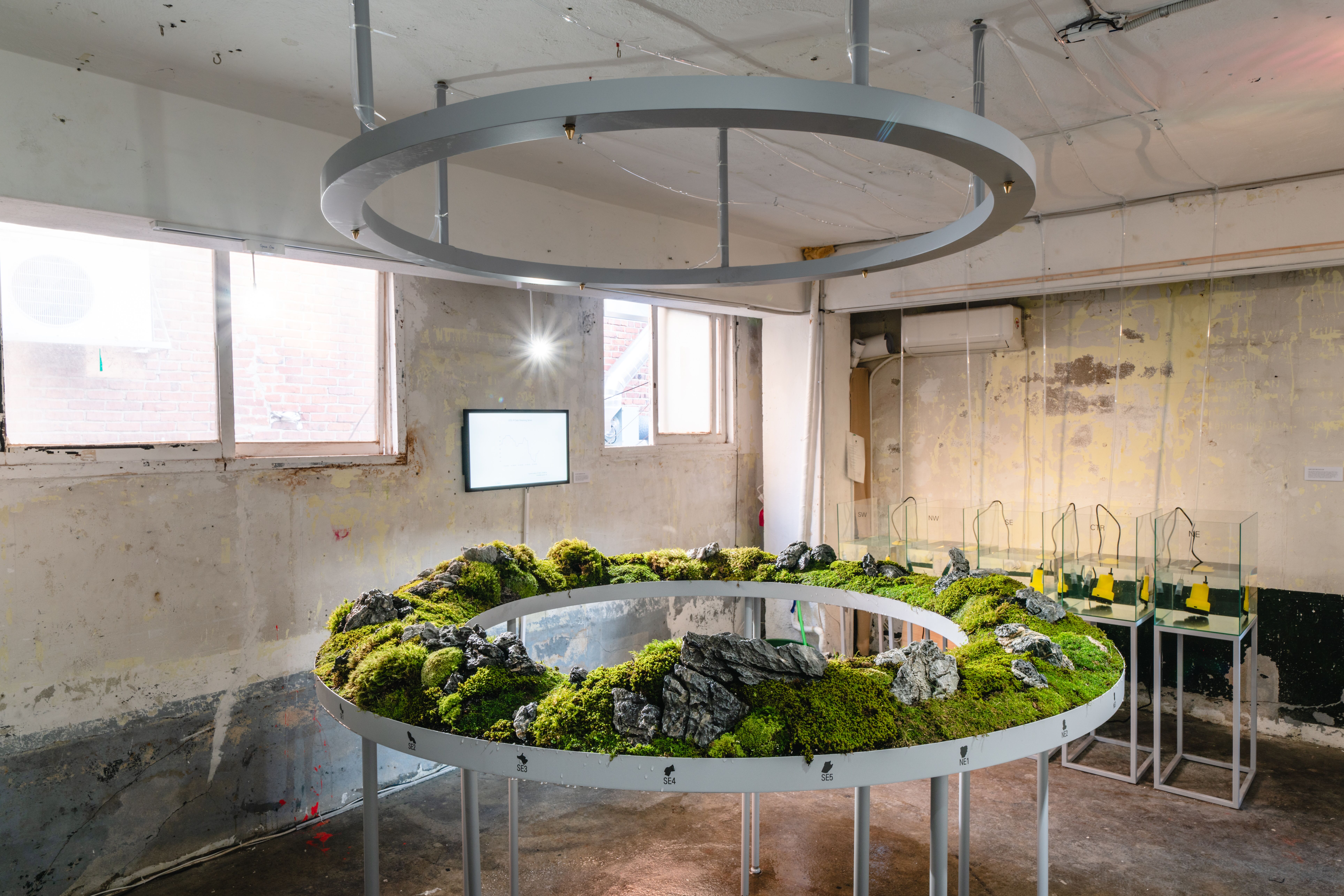
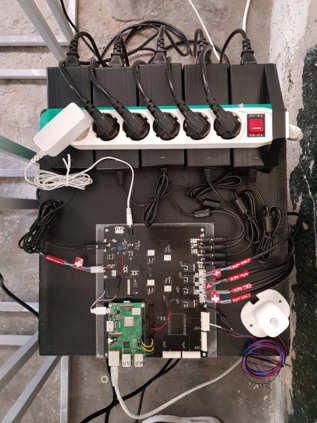


 Visualization of data using on-site fine dust sensor
Visualization of data using on-site fine dust sensor
Starting from 2018, when it will be at Urban Data Science Lab (UDSL) of Seoul National University, it is currently developing a platform for Nephhelometry sensorsand MSN (Massive Sensor Network) IoT sensorbased on MEMS sensors. In this work, a prototype of a sensorplatform under development in cooperation with a research team led by Professor Lee Dong-joonof Seoul National University was used to collect and visualize fine dust data at the gallery site in real time.

Visualization of fine dust data using augmented reality (AR)
Augmented reality is a technology that overlaps three- dimensional virtual images or objects in the actual image or background of the present real world that users see with their eyes and shows them as a single image. We developed it in Unity environment using an augmented reality platform called Vuforia. If you target images using AR app (aimagine) on a marker representing different districts of Seoul City, you can experience augmented reality by showing average fine dust levels for each year of 2017, 2016 and 2015.
Augmented reality is a technology that overlaps three- dimensional virtual images or objects in the actual image or background of the present real world that users see with their eyes and shows them as a single image. We developed it in Unity environment using an augmented reality platform called Vuforia. If you target images using AR app (aimagine) on a marker representing different districts of Seoul City, you can experience augmented reality by showing average fine dust levels for each year of 2017, 2016 and 2015.